Medical Emergency
If you are experiencing severe breathing difficulty or complete airway obstruction, call 911 immediately or go to the nearest emergency room.
Understanding Laryngospasm
A comprehensive guide to laryngospasm, a sudden involuntary spasm of the vocal cords that can cause breathing difficulties and distress.
Laryngospasm is a sudden, involuntary contraction or spasm of the vocal cords (laryngeal muscles) that temporarily blocks the airway. This condition can cause partial or complete obstruction of breathing, leading to feelings of choking, panic, and respiratory distress.
The larynx, commonly known as the voice box, contains the vocal cords which normally open during breathing and close during swallowing or speaking. During a laryngospasm episode, these vocal cords involuntarily clamp shut, preventing air from flowing through the airway.
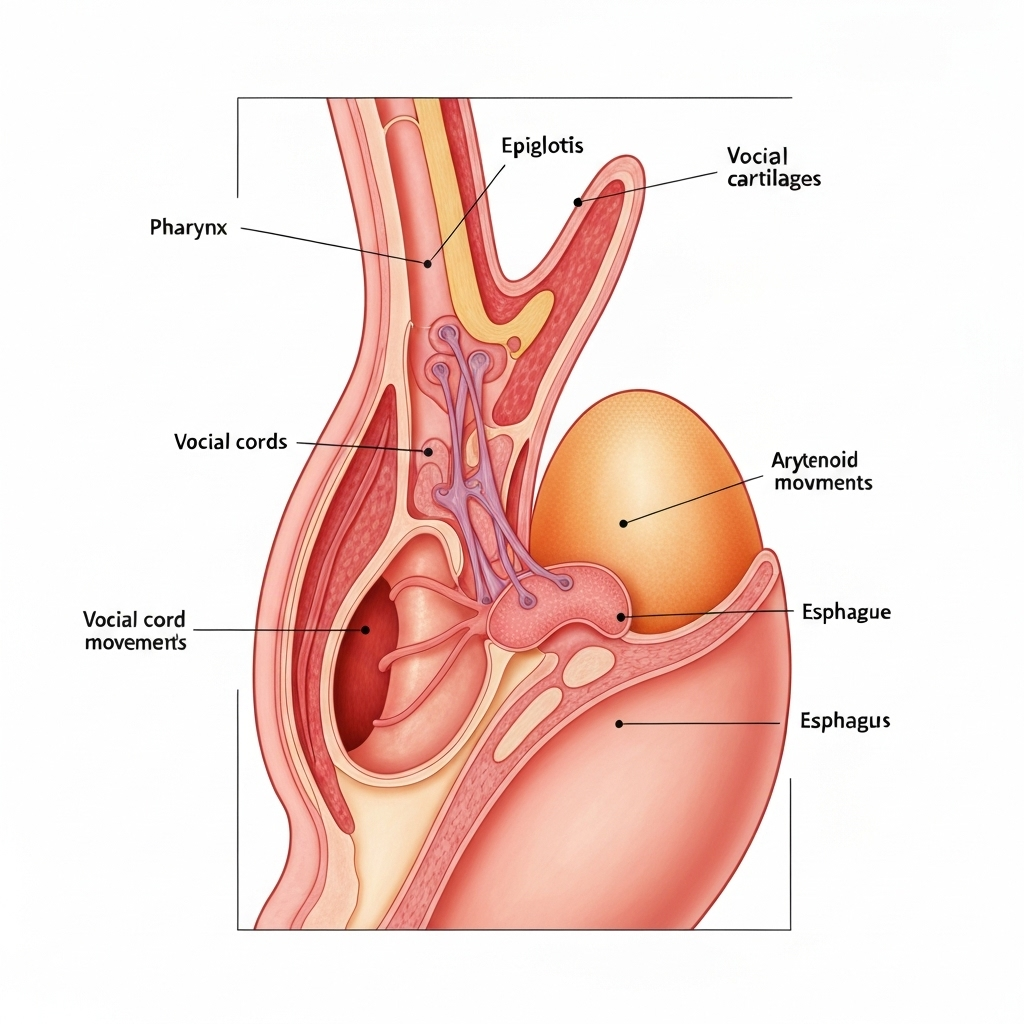
Key Structures
- Vocal Cords (True Vocal Folds): Two bands of muscle tissue that vibrate to produce sound
- False Vocal Folds: Located above the true vocal cords, help protect the airway
- Epiglottis: Cartilage flap that covers the larynx during swallowing
- Arytenoid Cartilages: Control vocal cord movement and tension
- Cricoid Cartilage: Ring-shaped cartilage forming the base of the larynx
Partial Laryngospasm
- • Incomplete closure of vocal cords
- • Some air can still pass through
- • May cause stridor (high-pitched breathing sound)
- • Less severe but still distressing
Complete Laryngospasm
- • Total closure of vocal cords
- • No air can pass through
- • Silent - no breathing sounds
- • Medical emergency requiring immediate intervention
Data from peer-reviewed medical literature and clinical studies
Medical Disclaimer
This information is for educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare provider for diagnosis and treatment of laryngospasm or any other medical condition. If you experience severe breathing difficulties, seek immediate emergency care.