When to Call 911
Complete inability to breathe, blue lips or fingernails (cyanosis), loss of consciousness, or severe respiratory distress requires immediate emergency medical attention.
Laryngospasm Symptoms & Diagnosis
Understanding the signs, symptoms, and diagnostic process for laryngospasm to ensure prompt recognition and appropriate medical care.
Respiratory Symptoms
- Sudden breathing difficulty
Inability to inhale or exhale normally
- Stridor
High-pitched breathing sound during inspiration
- Feeling of choking
Sensation of throat closure or obstruction
Associated Symptoms
- Panic or anxiety
Fear response to breathing difficulty
- Cyanosis
Blue discoloration of lips, fingernails, or skin
- Loss of voice
Temporary inability to speak or make sounds
Onset (0-5 seconds)
Sudden vocal cord spasm, immediate breathing difficulty
Peak Symptoms (5-30 seconds)
Maximum airway obstruction, panic response, possible cyanosis
Resolution (30 seconds - 2 minutes)
Gradual vocal cord relaxation, breathing normalizes
Clinical Assessment
Medical History
- • Previous episodes and triggers
- • Associated medical conditions
- • Medications and allergies
- • Recent surgeries or procedures
Physical Examination
- • Neck and throat inspection
- • Respiratory assessment
- • Neurological evaluation
- • Voice quality assessment
Specialized Tests
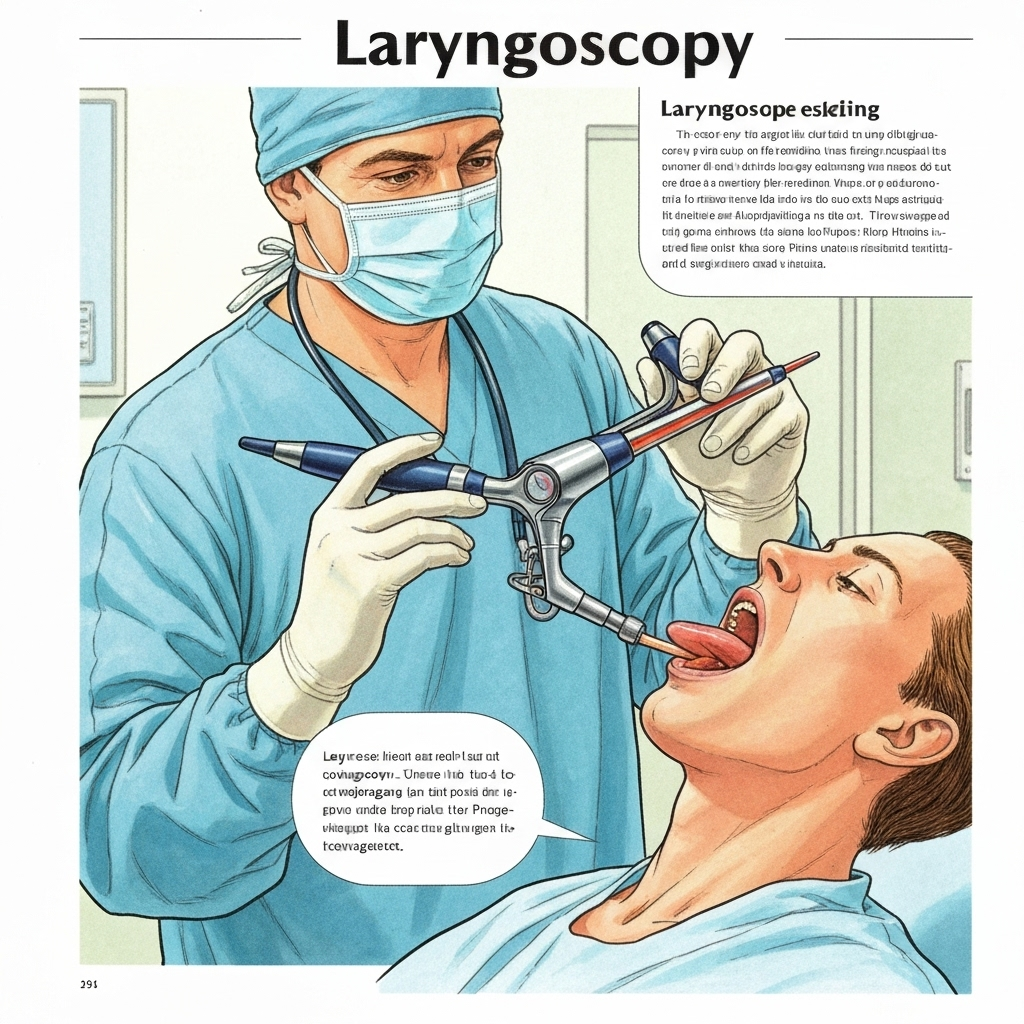
Laryngoscopy
Direct visualization of vocal cords using a flexible or rigid scope to assess structure and function.
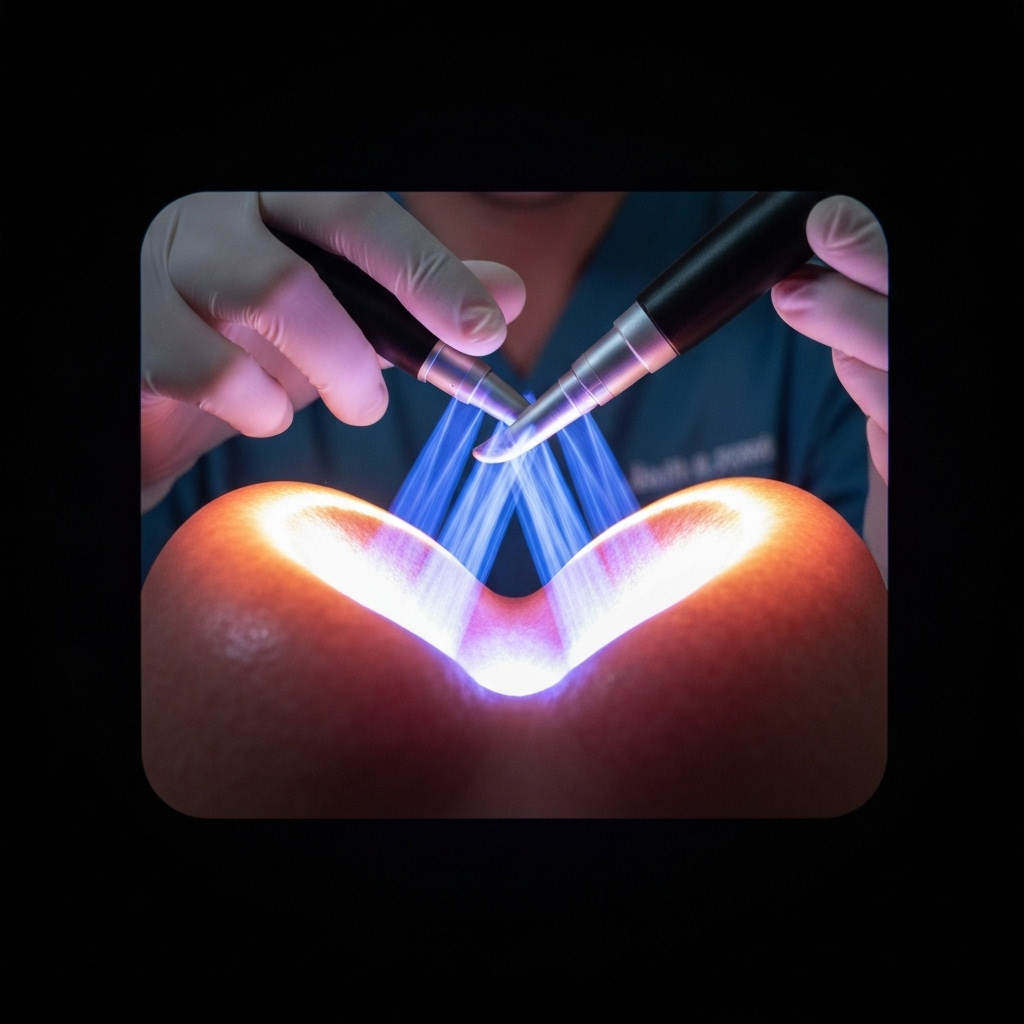
Stroboscopy
High-speed imaging to evaluate vocal cord vibration patterns and detect subtle abnormalities.
Healthcare providers must distinguish laryngospasm from other conditions that cause similar symptoms:
Similar Conditions
- Vocal Cord Paralysis
Permanent or temporary loss of vocal cord movement
- Asthma Attack
Lower airway constriction with wheezing
- Anaphylaxis
Severe allergic reaction with airway swelling
Key Differences
- Sudden Onset
Laryngospasm occurs abruptly, unlike gradual asthma
- Upper Airway
Obstruction at vocal cord level, not bronchi
- Self-Limiting
Usually resolves spontaneously within minutes
Call 911 Immediately
- • Complete inability to breathe
- • Blue lips, fingernails, or skin
- • Loss of consciousness
- • Severe respiratory distress
- • Episode lasting more than 2 minutes
Seek Urgent Care
- • Frequent recurring episodes
- • Episodes triggered by specific activities
- • Associated with other symptoms
- • Concerns about breathing patterns
- • Need for preventive strategies
Medical Disclaimer
This information is for educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Symptoms can vary significantly between individuals. Always consult with a qualified healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment. If you experience severe breathing difficulties, seek immediate emergency care.